Pressure Testing Methods for Shutoff Valves
How to pressure test a sanitary shutoff valve?
Sanitary shutoff valves play a critical role in almost any fluid, gas, or slurry system. We depend on shutoff valves to provide dependable on and off functionality and specific flow rates in residential, commercial, and institutional applications. While many are utilized routinely, they can also provide safety measures in emergency situations to prevent further outflow. This is why it’s so important to pressure test a sanitary shutoff valve.
The strength test for sanitary shut-off valves is very similar to the pressure testing methods for diaphragm valves. To pressure test a sanitary shutoff valve, we usually put assembled valves in the pressure testing rack, open the valve flap, pour in the medium to the specified value, and check for any leakage at the valve body and valve cover. The strength test can also be conducted individually.
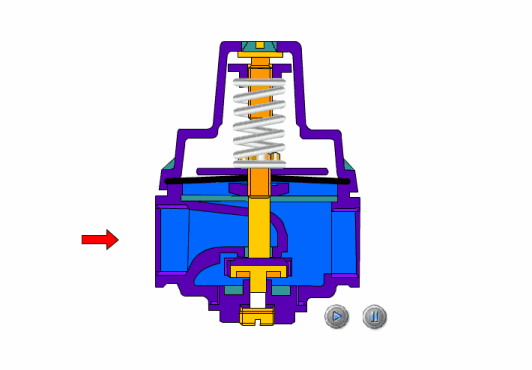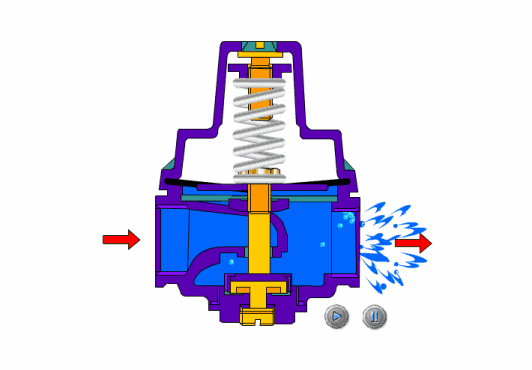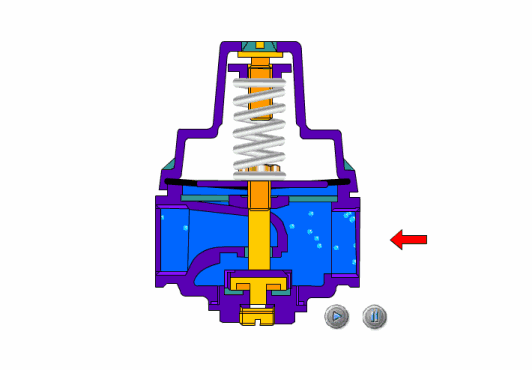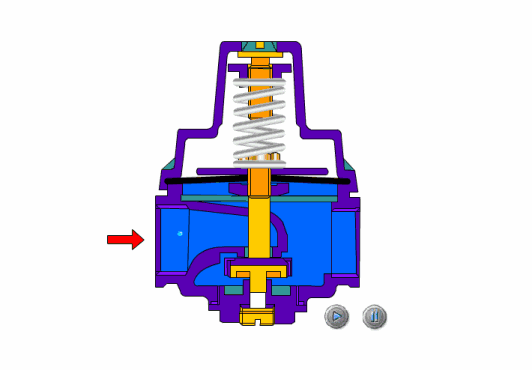
how to pressure test a shutoff valve
For the sealing performance test, place the valve stem of the shut-off valve in a vertical position. Open the valve flap and introduce the fluid or gas medium to the specified value from the bottom of the valve flap. Check the stuffing and gasket. Close the valve flap after the valve is qualified, and open the other end to check for any leakage.
If both the strength test and sealing performance test need to be conducted, we can first conduct the strength test, then lower the pressure to the specified value of the sealing performance test. Check the stuffing and gasket. Then close the valve flap, and open the outlet to check if there is leakage at the sealing surface.
Pressure test method of shut-off valve and throttle valve
For the strength test of the shut-off valve and throttle valve, the assembled valve is usually placed in the pressure test frame, the valve disc is opened, the medium is injected to the specified value, and the body and bonnet are checked for sweating and leakage. The strength test can also be carried out on a single piece.
The shut-off valve is used for the sealing tests. During the test, the valve stem of the stop valve is in a vertical position, the valve disc is opened, and the medium is introduced from the lower end of the valve disc to the specified value. Check the packing and gasket. After passing, close the disc and open the other end to check for leakage. If the valve strength and sealing test are to be done, the strength test can be done first and then depressurized to the specified value of the sealing test. Check the packing and gasket, then close the valve disc and open the outlet end to check whether the sealing surface leaks.
How does a shutoff valve work?
Shut-off valves rely on the pressure of the valve stem to force the sealing surfaces of the valve flap and the valve seat fit tightly together and prevents the medium from flowing through.
Sanitary shut-off valves only allow one-way flow of the medium and require directional installation. Structurally, they are usually longer than gate valves and they offer higher fluid resistance. However, the sealing reliability is not great for extended durations, which is why they are normally used for emergency shutdown situations. There are three types of shut-off valves: straight-through, right angle, and straight-flow oblique type.
What is the purpose of a shutoff valve?
The shutoff valve is one of the most widely used types of valves and plays the important role of cutting off and throttling the medium in the pipeline. Shutoff valves are often used for quick system shutdown in emergency situations. Its biggest advantage, and the reason why it is so popular, is the low-friction performance of sealing surfaces throughout the opening and closing process. With a narrow opening and durable design, they are easy to manufacture, install, and maintain. It is not only suitable for medium and low-pressure applications but also works reliably in high-pressure systems.
Conclusion
One key feature of shutoff valves is their plug-in disc which is flat or conical on the sealing surface. The disc moves along the centerline of the valve seat in a straight line. It can be used to control the flow of air, water, steam, various corrosive media, mud, oil, liquid metal, and radioactive media. This type of shut-off valve is very suitable for cut-off, regulation, and throttling. The opening or closing stroke of the valve stem is relatively short, and it has a very reliable cut-off function. Because the change of the valve seat opening is directly proportional to the stroke of the valve disc, it is very suitable for regulating the flow of fluids and gases.






