The Mechanism and Structure of Solenoid Valve
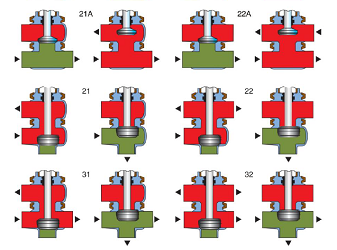
What are the types of solenoid valves?
Tracing the history of the development of the solenoid valve, so far, it can be divided into three categories according to its mechanism. These are direct-acting type, distributed direct-acting type, and pilot type. And according to the differences in the structure of the valve flap, materials, and mechanism, they can be divided into six sub-categories.
They are direct-acting diaphragm structure, distributed diaphragm structure, pilot diaphragm structure, direct-acting piston structure, distributed direct-acting piston structure, and pilot piston structure.
Direct-acting solenoid valve
Mechanism:
When the power is on, the electromagnetic coil generates electromagnetic force to lift the closing member from the valve seat and the valve opens. When the power is off, the electromagnetic force disappears, and the spring presses the closing member onto the sanitary valve seat, and the valve closes.
Features:
It can normally work in a vacuum, negative pressure, and zero pressure situation, but the diameter is generally less than 25mm.
Distributed direct acting solenoid valve
Mechanism:
It is a combination of direct-acting type and pilot type. When there is no pressure difference between the inlet and outlet, after the power is on, the electromagnetic force directly lifts the pilot valve and closing member of the main valve upwards successively, and the valve opens. When the starting pressure difference is achieved between the inlet and outlet, after the power is on, the pressure in the lower chamber of the pilot valve and main valve rises, while the pressure in the upper chamber drops, so the pressure difference pushes the main valve open; when the power is off, the pilot valve pushes the closing member down using the force of the spring or the pressure of the medium to have the valve closed.
Features:
It can act reliably in zero pressure difference, vacuum, and high-pressure situations. But the power is relatively large, and it must be horizontally installed.
Pilot solenoid valve
Mechanism:
When the power is on, the electromagnetic force opens the pilot hole and the pressure in the upper chamber decreases rapidly, forming a pressure difference around the closing member. The fluid pressure pushes the closing member to move upward, and the valve opens; when the power is off, the force of the spring closes the pilot hole, forming a pressure difference around the closing member with the inlet pressure rapidly passing through the bypass hole. The fluid pressure pushes the closing member to move downward, and the valve closes.
Features:
The upper limit of the fluid pressure range is high, and it can be installed in any position while meeting the requirements of fluid pressure difference.
Conclusion
A solenoid valve is used to open, close, mix, or divert media in an application. They are used in a wide variety of applications from dishwashers, cars, and irrigation. Thank you for reading our article and we hope it can help you better understand the mechanism and structure of the solenoid valve. If you want to learn more about solenoid valves, we would like to advise you to visit Adamant Valve homepage for more information.




