The Comparison Between Solenoid Valves and Electric Valves

What is the difference between solenoid valves and electric valves?
Specifying the differences between the solenoid and electric valves can be a confusing task because both function similarly. However, the experts at Adamant Valves were kind enough to explain the 4 key differences between these two types of sanitary valves. We shared their information in the list below. Let’s dive right in to learn more about solenoids and electric valves!
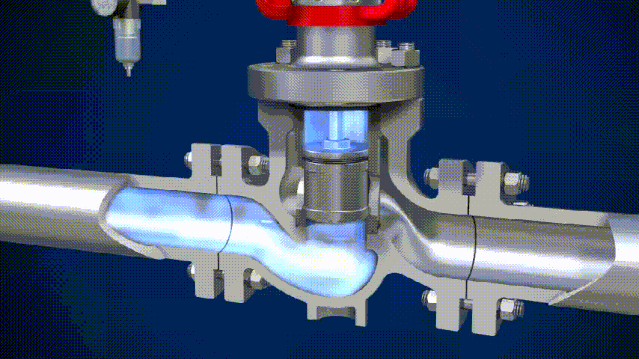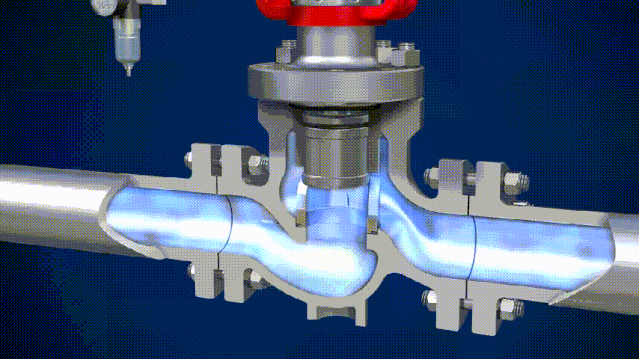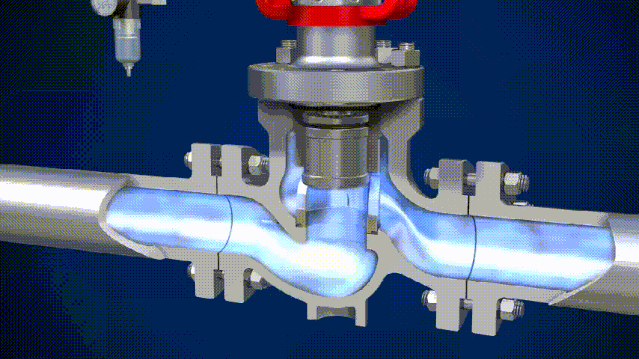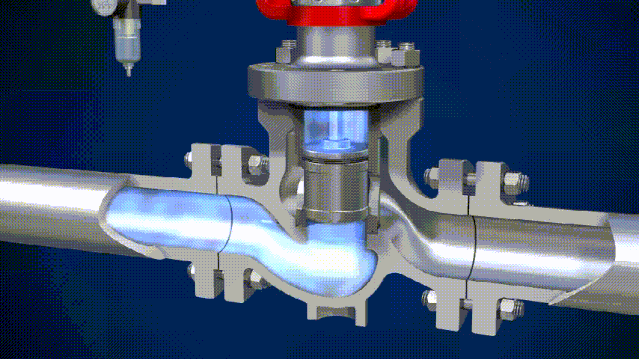
The 4 Main Differences Between Solenoid Valves and Electric Valves
1. Differences in Valve Function:
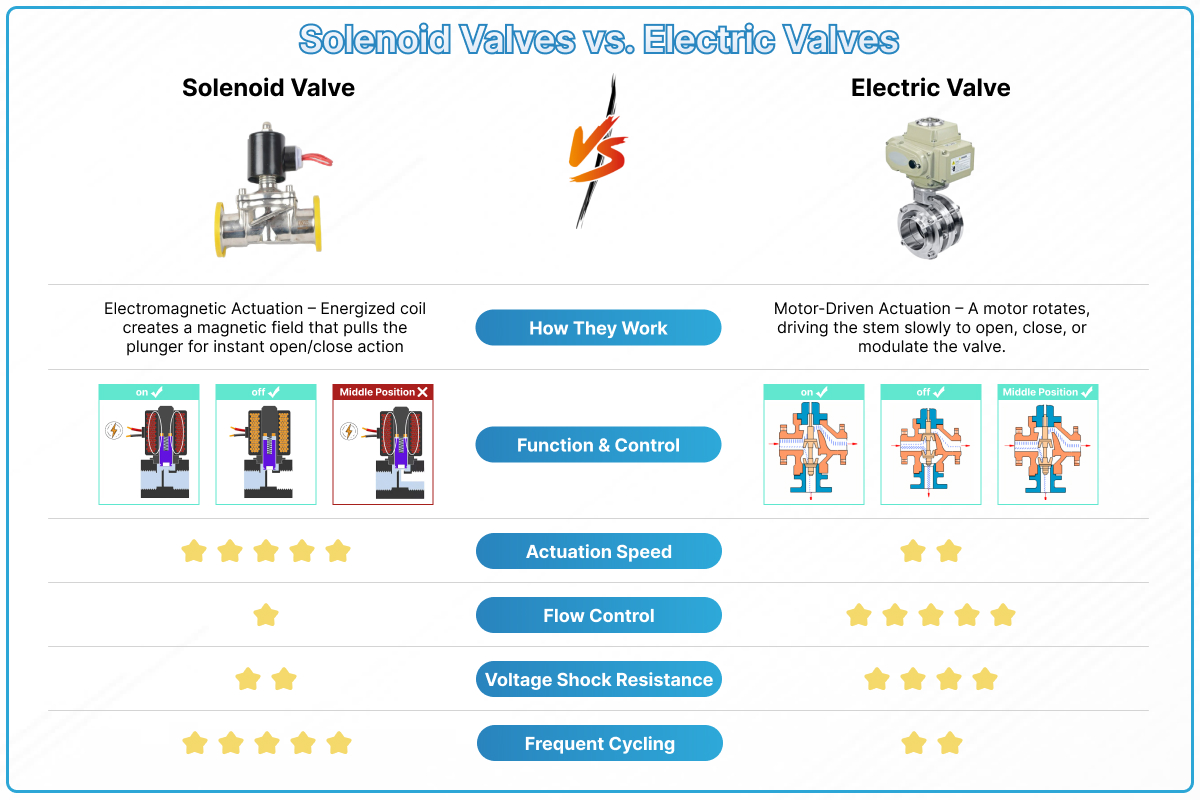
Electric valves usually actuate using force from motors which are more resistant to voltage shock than solenoids. Solenoid valves open and close faster than electric valves, so they are usually used in applications with frequent switching between open and closed positions, or in applications with low flow rates and low pressure.
Solenoid valves actuate with an electromagnet. When an electric current is applied to the coil, it generates a magnetic field that pulls a metal armature against spring force, thereby opening or closing the valve. Thanks to their electric activation, they are often used in fluid process systems that require computer connection and automated controls.
With electric valves, you can control the degree to which the valve opens or closes, meaning there are three (or more) states: open, closed, and half-open/half-closed. The half-open position provides some control over the flow rate of the medium in the pipeline. Solenoid valves can’t meet this requirement.
Usually, the solenoid valve has a very small flow coefficient and working pressure difference. Solenoid valves are actuated by an electromagnetic coil, so it’s more susceptible to damage from voltage shock. Another advantage of solenoid valves is that they can be reset when the power is off while a reset device needs to be installed on the electric valve to achieve such a function.
2. Differences in Actuation Method:
Electric valves are actuated, or opened and closed, by motors. It takes a certain amount of time for the opening or closing action to complete, meaning that electric valves are not particularly suited for applications that require rapid actuation. Solenoid valves are actuated by an electromagnetic coil and can be opened or closed faster than electric valves. The solenoid’s quick actuation makes it adept at controlling fluids, gases, and steam.
3. Different Applications:
The electric sanitary valve is generally used to regulate and switch systems on and off. They’re often found in fan coil ends, and their versatile function makes them suitable in many different applications.
Solenoid valves are used to shut off, release, dose, distribute or mix fluids. They’re suitable for some special processing requirements, such as leakage of the fluid medium. They’re generally more expensive than electric valves because they require electromagnetic components and some have sophisticated online connectivity.
4. Various Applicable Processes:
Solenoid valves can meet special technical requirements and are often custom-made to the consumer’s specifications. For these reasons, they are usually priced more expensive than electric valves. Electric valves are generally used for regulating, and also for switching, such as in the fan coil terminal.
The general flow coefficient and the working pressure difference of the solenoid valve are small. The solenoid valve is driven by the electromagnetic coil, which is easily damaged by voltage impact. It is equivalent to the function of the switch. However, the electric valves are usually driven by motors, which are relatively resistant to voltage impact. And the opening and closing of the electric valve can be controlled. It can control the flow of the medium in the pipeline, but the solenoid valve can’t meet this requirement.
Comparing Electric Valves with Solenoid Valves
When you compare electric valves and solenoid valves side by side, you’ll find there are four fundamental differences between the two. While these critical valves are very similar in function, they differ in their function, actuation, application, and processing capabilities. If you’re curious to learn more about these two types of valves, please visit the Adamant Valves home page and contact us.





Quite an informative post! In my view, the key distinction between the two is that the electrical valves are operated by a motor whereas the solenoid valves are powered by an electromagnetic coil. Furthermore, in the event of a power outage, the solenoid valve may be quickly reset, whereas the electric valve requires a device.
It’s nice that you pointed out how solenoid valves could meet special technical requirements and are usually custom-made to the consumer’s specifications. I was chatting with my friend the other day and he briefly mentioned solenoid valves due to his work. It got me curious about the valve so I looked into it and it is more sophisticated than I thought, which was quite interesting.