The post What is a Sanitary Ball Valve and How Does it Work? appeared first on Adamant Valves.
]]>Sanitary ball valves, also called hygienic ball valves are opened by turning handles attached to balls inside the valves.

Adamant valves can supply valve body and disc materials such as AISI 304 or AISI 316L, 304L, and 316 materials according to your requests. This hygienic ball valve is suitable for dairy, food, beer, beverage, pharmaceutical, cosmetics, and other industrial areas.
Adamant valves sanitary ball valves are made of high-quality stainless steel, which can meet the special requirements of various media in the food and biopharmaceutical fields. The smooth, seamless, and automatic emptying of handicrafts is also very suitable for steam cleaning.
How does it work?
Sanitary ball valves can be opened by turning handles attached to balls inside the valves. The valve body is a ball, the ball has a hole or port through the middle. When the port is in line with both ends of the valve, the flow will occur.
When the valve is closed, the hole is perpendicular to the ends of the valve, and flow is blocked. A ball valve is durable and suitable to achieve perfect shutoff and flow control purposes even after years of disuse.
What are the types of sanitary ball valves?
Ball valve classification according to the assembly structure, can be divided into three commonly used designs: one-piece, two-piece, and three-piece housings. The difference is how the ball valve is assembled:
One-piece —The valve parts are pressed or welded. The diameter of the ball is slightly smaller than that of the pipe. The valves can not be opened for cleaning or maintenance.
Two-piece — Two-piece ball valve is composed of two parts, the sealing effect is better than a one-piece ball valve, the diameter of the ball and pipe diameter of the same, and the one-piece ball valve is easy to remove. Usually, the parts are connected via a threaded connection. The valve must be completely removed from the pipe in order to separate the two parts.

Three-piece — Three-piece ball valve is composed of three parts, a valve cover, and an intermediate valve body, the parts are generally clamped together by bolt connections, and it is easy to remove and maintain.
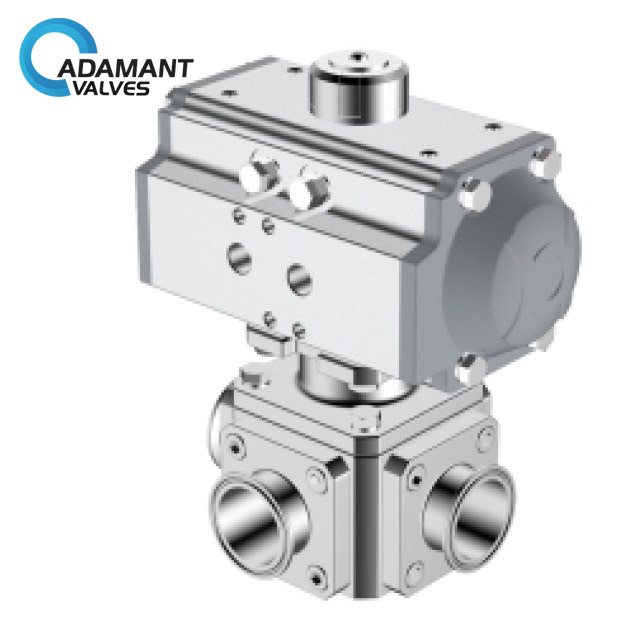
Ball valve classification is according to the hole of the ball, such as reduced bore, full bore, and V-shaped.
Reduced bore — Most ball valves have a reduced bore. One-piece ball valves are almost always reduced bore.
Full bore — Full bore valves have the same bore diameter as the pipe. The advantage is that there is no additional friction loss and the system is mechanically easier to clean. The disadvantage is that the ball and the housing are bigger than a standard ball valve with a reduced bore.
V-shaped — The hole in the ball or the valve seat has a “V” shaped profile, the required flow can be controlled more precisely by rotating the ball.
The post What is a Sanitary Ball Valve and How Does it Work? appeared first on Adamant Valves.
]]>The post What is the Best 3 Way Sanitary Valve for Wine? appeared first on Adamant Valves.
]]>
For this wine, the process begins during the 4-week fermentation process where each tank of grapes is tasted twice a day. When this process comes to a close, samples are drawn from each tank and evaluated to decide if they are “blend worthy”.
Once the lots are selected, the wines are blended together in upright, 6,000-gallon oak crests. With these blends being drawn from as many as 30 different lots, it is critical to have the most reliable wine manufacturing process in place. For these reasons, the Three-Way Sanitary Ball Valve was chosen.
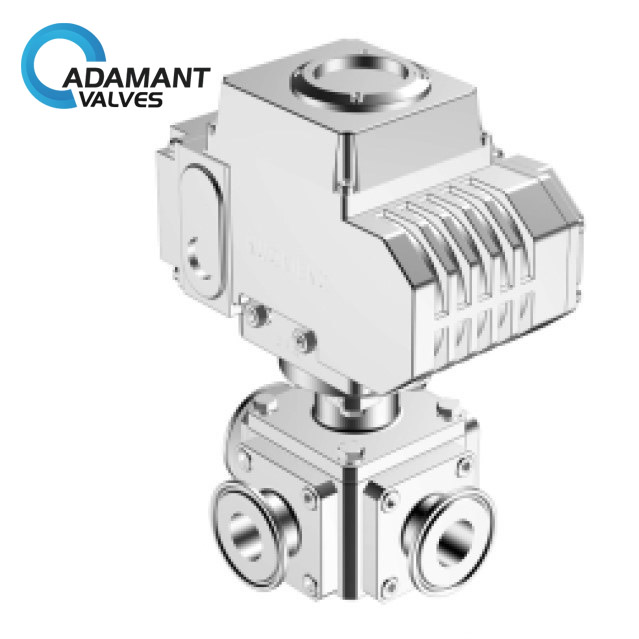
Adamant’s Three-Way Sanitary Ball Valves meet health and safety requirements for industries that require thorough cleanliness and the absence of contamination. This food-grade valve provides flow control for raw ingredients as well as finished products, making it ideal for the meticulous wine blending process. Adamant’s unique Three-Way Sanitary Ball Valve features a direct mount actuator pad and high cycle stem seal design, making it suitable for a wide range of process applications.
If you would like to learn more about Adamant’s Sanitary Valve options, please reach out to our sales team for assistance.
The post What is the Best 3 Way Sanitary Valve for Wine? appeared first on Adamant Valves.
]]>The post What is a 3 Way Sanitary Ball Valve Used for? appeared first on Adamant Valves.
]]>
Adamant sanitary provides sanitary 3-way ball valves with full bore or reduced bore design, in stainless steel 304 or 316L with different connection end.
Stainless steel sanitary 3-way ball valves are used in a wide variety of high-pressure applications.
The sanitary ball valve is compact and simple in design, and easy to maintain, with a full diameter from 1/2″ to 4″, and meet the stringent requirement of high-purity sanitary industries of Food, Brewery, Beverage, Dairy, Pharmaceutical, Biopharma, etc.
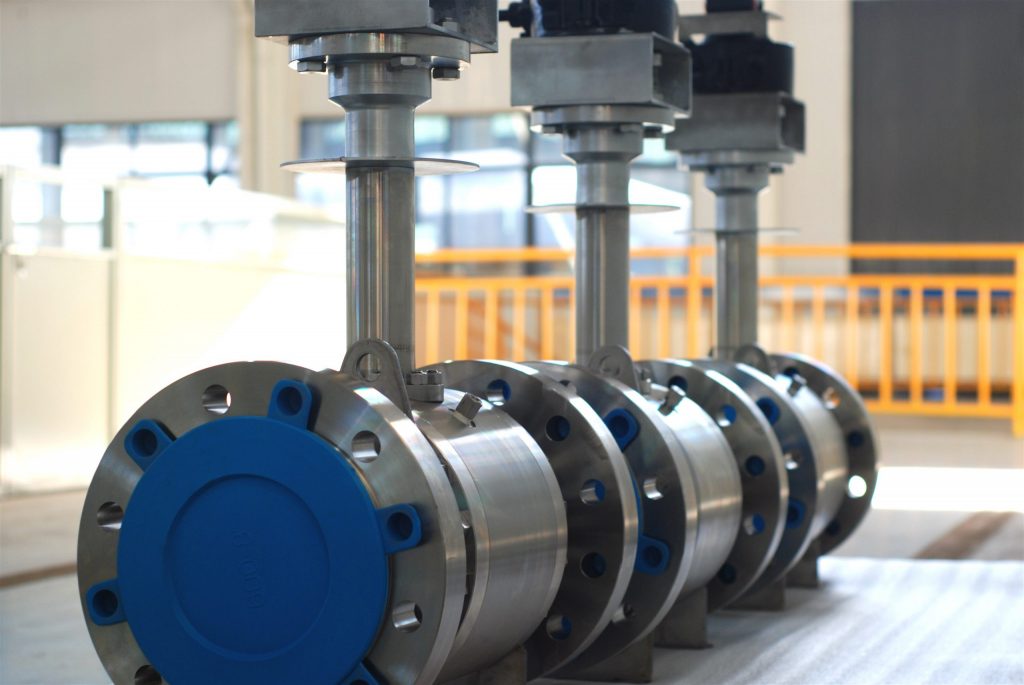

A full, unrestricted flow allows no product restrictions through the valve, allowing easy diversion. We offer three-way ball valves made of T316 (CF8M) stainless steel with PTFE seats that are easily removed.
Clamp and weld ends are standard. Other connections are available upon request. Ball valves meet 3A requirements. L-Port is standard, but T-Port is available upon request.
Stainless steel sanitary 3-way ball valves are used in a wide variety of high-pressure applications. A full, unrestricted flow allows no product restrictions through the valve, allowing easy diversion.
We offer three-way ball valves made of T316 (CF8M) stainless steel with PTFE seats that are easily removed. Clamp and weld ends are standard. Other connections are available upon request. Ball valves meet 3A requirements. L-Port is standard, but T-Port is available upon request.
The post What is a 3 Way Sanitary Ball Valve Used for? appeared first on Adamant Valves.
]]>The post Are Sanitary Ball Valves Good for Flow Control? appeared first on Adamant Valves.
]]>The ball valve is mainly used in pipelines to cut off, distribute and change the direction of media flow, and designed as a V-shaped opening ball valve also has a good flow regulation function.
Which ball valve is best?
One of the answers is Sanitary 3-way Ball Valves.
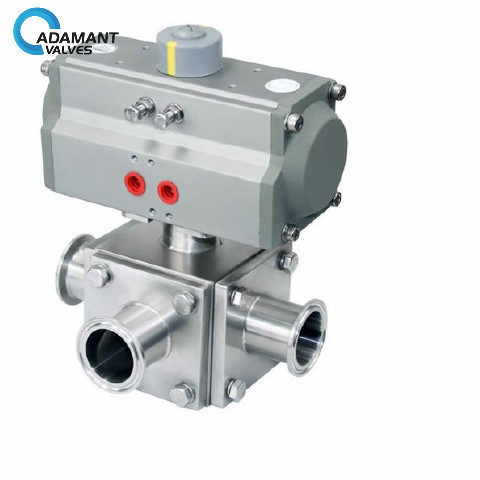

The main characteristics of Sanitary Ball Valves are its own compact structure, reliable sealing, simple structure, sealing surface and the spherical surface is often in a closed state, not easy to be eroded by the medium, easy to operate and maintain, suitable for water, beer, pharmaceuticals, and other sanitary working media, widely used in various industries.
Sanitary Ball Valve is a sphere, it is the ball around the center line of the valve body for rotation to achieve opening, or closing a valve. The pipeline is mainly used to cut off, distribute and change the flow direction of the medium.
Why are sanitary ball valves better?
1, small fluid resistance, the full diameter of the ball valve basically no flow resistance.
2, simple structure, small size, and lightweight.
3, good sealing, in a wide range of pressure and temperature, can achieve a complete seal.
4, easy to operate, can achieve rapid opening and closing, can be used in the automatic control system, easy to control from a distance.
5、The valve body is symmetrical and can well withstand the pressure from the pipeline.
6, easy to maintain, the ball valve structure is simple, the seal is generally movable, and easy to disassemble and replace.
7, long service life, in fully open and fully closed, the ball and seat sealing surface is isolated from the medium, so the high speed through the valve medium will not cause erosion of the sealing surface.
What are the specification sizes of sanitary Ball valves?
1、Nominal pressure or pressure level: PN1.0-32.0MPa, ANSICLASS150-900, JIS10-20K.
2、Nominal diameter or caliber: DN6~900, NPS1/4~36.
How do I know what size sanitary ball valve I need?
The larger the size of the bore, the better the flow rate so this is a good place to begin, especially if you are specifying a new assembly that will include your sanitary ball valve. If the rate of flow within your process system is optimized with a 2” hose then it is likely that you will require a 2” sanitary ball valve to suit.
The post Are Sanitary Ball Valves Good for Flow Control? appeared first on Adamant Valves.
]]>The post The Ultimate Guide to Bio-Pharmaceutical Sanitary Valves appeared first on Adamant Valves.
]]>Every industry has a demand for sanitary fittings, but the pharmaceutical industry takes the crown in this race. There is very little margin of error in this industry, as we are talking about medicines. Medicines that cure our headaches, medicines that save our life! As it is evident, the standard sanitary fittings aren’t meant for manufacturing drugs. Hence, there is a need for biopharmaceutical sanitary valves, which we are going to discuss in this brief. Biopharmaceutical fittings (BPE) are a perfect solution to this problem.

The Difference Between Sanitary Valves and Industrial Valves
On the face of it, there seems to be very little difference between biopharmaceutical fittings and 3A sanitary fittings. However, there are some critical differences in the styles of the two fittings that set them apart. The BPE fittings comply with the ASME-BPE standards. It is pertinent to mention it again that sanitary valves play a critical role in the production of pharmaceutical products. Therefore, it is natural that these vales feature high tolerance and clean interior surface finishes. This is in contrast to standard fittings. Furthermore, material requirements are a lot different than 3A sanitary standards. 3A standards are industrial valves that find plenty of uses in industries like food, beverage, and dairy.
What are the Main Types of Sanitary Valves?
Fun fact: It is possible to build sanitary valves with thousands of variations! However, for the sake of convenience, we can classify sanitary valves into three key types. This classification is made on the basis of their mechanical motions. These three classes are linear motion, rotary motion, and quarter-turn valves. Let us talk about them briefly in the following lines of this brief:
1. Linear Motion Valves
These valves use a closing member. As they move in a straight line, they permit, stop or choke the medium’s flow. You might have come across some types of linear motion valves already. These include gate, diaphragm, pinch, lift check valves and globe valves.
2. Rotary Motion Valves
In this type of sanitary valve, a valve closure member is used. It is this valve that permits motions on the cylindrical or angled paths. Some of the common types of rotary motion valves include ball, eccentric, swing check, and butterfly valves.
3. Quarter Turn Valves
In essence, these are just like rotary motion valves. The key point to note here is that these valves require only a quarter-turn stem motion to switch their positions between fully open and fully closed.
An important that must be kept in mind is that a sanitary valve is defined by a set criterion. Unless these special sterile requirements are met, a valve cannot be deemed sanitary.
Let us talk a bit about the sanitary ball valves and butterfly valves in this space as well. Coming towards the sanitary ball valves first, well, they use a ball with a hole that is drilled through the middle swivel mounted to the valve body. The sanitary ball valves operate at their maximum when the ball is in line with the pipe. However, it is quite possible to rotate the hole in the ball away from the pipe’s direction. This chokes the flow rate. It is cut off completely once the hole is at 90 degrees in the pipe direction.
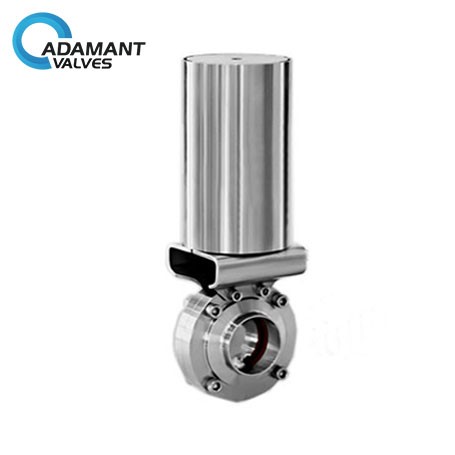

Often, there is a question about the nature of the butterfly valves. Do they have a place in the sanitary club or not? The answer is, yes, of course, they are sanitary valves. They feature a single eccentric structure. Their soft seal is predominantly different from the middle section. Their characteristic features are compactness, lightweight and minimalistic composition.
Who Uses Sanitary Valves and Why?
Now, let us talk a bit about the end users of sanitary valves. Usually, biopharmaceutical sanitary valves are used by folks concerned with the pharmaceutical industry, biotechnological facilities, and certain other purity industries. What makes them suitable for use in these industries? Let us find that out in this section of the discussion!
In medical industries, contamination is the last word you would want to hear. We don’t need to build on why it is a taboo word there, right? Now to the real point, if there are services in the valves, then the chances of contamination increase by a significant factor. So ideally, valves that come without any services sound like a perfect pick for industries that we have mentioned in the earlier lines of this brief, right? Guess what? Sanitary valves come without any services! So that contamination problem is solved alright, what do you think?
Cleaning is cumbersome sometimes. When we are talking about mega industries like the pharmaceutical industry, then we need to pay more attention to streamlining the process. That’s where sanitary valves save the day. Because they are not stained easily, they are a super convenient option. Now you might not realize it at first, but the extensiveness of the process is directly proportional to the amount of cleaning that needs to be done afterward!
Sanitary valve manufacturers in USA are making gold as they are a perfect pick for anyone who is weary of polishing and smoothing valves all the time. Do you know who that is? Pharma boys! Rust is enemy number one in all such settings. It can complicate things to a great extent. Hence, sanitary valves are a perfect pick again because they are made of polished stainless steel.
Standards & Certification
ASME-BPE
ASME has a BPE committee that acts as a governing body for BPE standards. The ASME-BPE standard is concerned with all aspects of BPE fittings. These aspects include tolerances, interior surface finishes, product markings, composition, and packaging. BPE certification implies that ASME has conducted an audit of a company. Companies that hold ASME-BPE certification can proudly flaunt that they are meeting the required standards. Such audits are a must for compliance. Companies who undergo the said audits have permission to label their products with ASME certification marks.
One of the key requirements of ASME-BPE standards is that the BPE fittings must be consistent in terms of dimensions. It doesn’t matter who is producing them; the manufacturer becomes an irrelevant topic in this discussion. Then, these sanitary valves must also come with specific permanent markings on the outside of the fittings. These markings include heat number, material type, company, manufacturing country, surface finish, and the letters BPE inscribed on them.
An important question that arises here is: how is material verification performed in the case of BPE fittings? Well, it is done so by using a niton gun. Thanks to this clever invention, identifying a fitting in terms of its chemical composition is fairly easy. All that it takes is a single click! Performing this identification is extremely important since, without it, one cannot be sure about the materials that the end-users are getting.
Traceability
Traceability is one of the most important factors when we are talking about BPE fittings. It is absolutely essential that the chemical and mechanical make-up of the materials must meet the set criterion. Otherwise, the sanitary valves in question will not be given the due nod of approval. Here, talking about heat numbers is a must; they identify the manufacturing lot of the steel. Normally, heat numbers are marked on the outer side of the sanitary valves. Heat numbers must match up with the corresponding paperwork. This corresponding paperwork is dubbed Materials Test Reports. It serves as proof that the sanitary valves meet the specified standards.
MTR
Let us talk about Material Test Report (MTR) in this domain as well. It is an official piece of documentation from the mill; it specifies the mechanical and chemical properties of the steel. Its importance in material traceability and verification cannot be ignored. The MTR must be provided with every sanitary valve. Sanitary valve suppliers need to take care of these parameters.
Conclusion
So, that would be all from this brief. As it is evident from these lines, the biopharmaceutical sanitary valves have critical importance in medicine and related pharmaceutical industries. Precision and fine finishes are key parameters that distinguish them from their industrial counterparts. To ensure that nothing wrong has happened throughout the process, documentation and packaging have been given due weightage as well. It is these major points that allow users to trace back products to inception. Once the understanding is at the most perceptive level, users can easily pick the sanitary valve that is the requirement of the process.
Today, the industrial web is bigger than ever. It is getting more and more specific with every day passing. Biopharmaceutical industries needed something safer and more efficient to solve their quality woes and concerns. Sanitary valves are the answer, as it seems!
The post The Ultimate Guide to Bio-Pharmaceutical Sanitary Valves appeared first on Adamant Valves.
]]>The post In Which Fields are Pneumatic Ball Valves Mainly Used and What are the Main Features? appeared first on Adamant Valves.
]]>
Definition
A valve is defined as “The generic name of a device with a moving part allowing it to open and close a passageway to allow, prevent or regulate the flow of a fluid.”
Valve Categories
There exist many types of valves in various technical industries. The most commonly used manual valves in steam systems and sanitary systems are globe valves, ball valves, slide valves, and butterfly valves.
Valves can be categorized as follows based on their construction and features:
- Ball valve or Butterfly valve – The valve element ‘swivels’ in the flow path to stop the flow.
- Globe valve – The valve element acts as a seal or plug in the passageway to stop the flow.
- Gate valve – The valve element is ‘inserted’ into the flow path to stop the flow.
- Diaphragm valve – The passageway itself is ‘throttled from the outside’ to stop a flow.
The construction of a gate valve is similar to that of a sluice. Another essential characteristic of this type of valve is the low-pressure loss when the valve is fully open. The valve body, however, must be lifted entirely out of the way for the valve to be fully open. This means that the lever must be turned frequently. Low-pressure loss is also present in this valve type because of the face-to-face dimension of a butterfly-type valve that is often tiny. These valves are often used in water and air applications.
Let’s take a closer look at ball valves and globe valves, two types of valves often used in steam systems.
Ball Valves
This type of valve features a polished ball with a hole in the center that rotates in the valve body. When the hole is aligned with the pipe, materials can flow through it. However, the ball cuts the flow when turned at right angles to the line. Because of their short actuation travel, motorized ball valves belong to a family of products called quarter-turn valves. This makes them very fast to operate and ideal for fast response cuts. The ball valves also offer exceptional shut-off values, the average arrangement of the balls ensuring a perfect seal.
Ball valves offer a very good shut-off and are practical because to open and close the valve; it is enough to turn the lever by 90°C. In addition, they can be a full bore, which means that the opening of the valve is the same size as the inside of the pipe. This generates a very low-pressure loss. Another feature is the lower likelihood of gasket leakage. This results from the valve stem only having to turn 90°C.
It should be noted, however, that this valve is intended for use only when it is fully opened or fully closed. It is not suitable for use in a partially open position for any application, including flow control. Thus, it is not ideal for use in a partially open position for any application, including flow control.
Globe Valves
The globe valve is suitable for various applications, from flow control to zero flow.
When the valve is tight against the valve seat, the valve is closed. This type of valve opens when it is moved away from the valve seat. So, flow regulation is not by the degree of opening of the valve seat but by the valve lift (distance between the valve and the seat). A feature of this type of valve is that, even if used in the partially open position, there is little risk of the fluid damaging the valve seat. The kind of globe valve mainly used for flow control is the needle valve.
It should be noted, however, that due to the S-shape of the passageway of this valve, the pressure drop is more significant than that observed with other types of valves. Also, the valve stem must be turned frequently to open and close the valve. Consequently, the gasket tends to leak. Also, because closing the valve involves turning the valve stem until it is seated firmly against the valve seat, it is difficult to determine the exact point at which the valve is fully closed. Cases have occurred where overturning the valve stem by accident has damaged the seating surfaces.
Pneumatic Ball Valves
Pneumatic valves, also known as pneumatically actuated angle seat valves or externally piloted valves, are an excellent choice when a conventional solenoid valve just won’t do.
Such a valve is a good troubleshooting solution for troublesome situations; it allows very high flow rates, can start operating from 0 differential pressure, and enable high temperatures of fluid. It can also perform to flow high viscosity and contaminated fluids. Moreover, it works in EEx zones simply by placing the pilot valve outside of this area. The valve is usually paired with a pneumatic actuator powered by a 3-way valve solenoid. Pilot fluid pressure flows into the actuator cylinder and acts on the piston, allowing the seal to open or close through the stem. The seal returns to its resting position using a return spring which is located in the pneumatic actuator.
Note that a ball valve is not pneumatic in and of itself. When someone refers to a “pneumatic ball valve,” they are referring to the commonly used ball valve that is fitted with a pneumatic actuator. The actuator is typically mounted to an industry-standard (ISO 5211) 4-bolt mounting pad on valves designed for automation.
Applications for pneumatic valves
A Pneumatic ball valve can be used in many applications:
- Cooling.
- Pre-Heating.
- Sterilizers and Autoclaves.
- High-Pressure Lubrication.
- Distributing Steam.
- Bottling.
- Textile Production Equipment.
- Industrial Steam Ironing Equipment.
- Mixture of Paints, Inks, and Colors.
- Industrial Washing and Cleaning Equipment.
Other applications of pneumatic valves
Pneumatic valves are used in the development of automation or remote-control systems. As such, they are found in all industry sectors, machine tools, chemicals, petrochemicals, medical, pharmaceuticals, food, transport, etc.
They can also be applied to communities: hot water, air or steam heating, air conditioning, transport of liquid or gaseous fuels, and fire-fighting.
The post In Which Fields are Pneumatic Ball Valves Mainly Used and What are the Main Features? appeared first on Adamant Valves.
]]>The post WHERE CAN I FIND THE BEST ELECTRIC ACTUATED BUTTERFLY VALVE MANUFACTURER IN THE USA appeared first on Adamant Valves.
]]>Valves have many uses, such as domestic uses for controlling water for irrigation, industrial uses for controlling processes, and residential uses such as on/off and pressure control to dish and clothes washers and taps in the home. Valves are also used in the military and transport sectors. Valves are found in virtually every industrial process, including water and sewage processing, mining, power generation, processing of oil, gas, and petroleum, food manufacturing, chemical, and plastic manufacturing, and many other fields. They provide several functions, such as starting or stopping fluid or liquid flow based on the valve state, regulating fluid or liquid flow and pressure within a piping system, controlling the direction of flow within a piping system, throttling flow rates within a piping system, improving safety through relieving pressure or vacuum in a piping system.
The common and popular kinds of valves include but are not limited to Gate Valve, Globe Valve, Check Valve, plug valve, Ball Valve, Butterfly Valve, Actuated valves, Needle Valve, Pinch Valve, Pressure Relief Valve, Air Logic valves, Balancing valves, Line Blind valves, Cartridge valves, Casing valves, Cock valves, Diaphragm valves to mention a few. These valves typically perform the same functions and they serve the same purposes as mentioned above, for starting and stopping liquid or fluid flow and so on. The major difference that differentiates the various types from one another is the mechanism in which they perform their functions. For instance, the gate valve works in a linear motion to achieve its purpose and function likewise is the pinch valve while on the contrary, the ball valve, plug valve likewise the butterfly valve works in a rotary motion.
This article places focus on the electric actuated butterfly valve. As a type of valve. First, the Butterfly valve is a quarter-turn rotational motion valve, it is mainly used to start, regulate, and stop fluid or liquid flow. A butterfly valve controls fluid or liquid flow by using a disk that turns on a diametrical axis inside a pipe or by two semicircular plates hinged on a common spindle, which allows fluid or liquid flow in only one direction. The butterfly valves are made in a short circular body and due to their compact and lightweight design which unlike other types of valves, does not consume space. The Butterfly Valve is suitable as it perfectly fits in large applications and tight space usages. Its key specifications include the port connection, the valve size, and the materials that make up the valve body, further key specifications include its seat, seal, disc, as well as its stem packing. The Butterfly valves are mostly used in wastewater plants, power plants, and process plants for shut-off and for regulating and isolating services. The butterfly valves are especially popular and commonly used in very large diameter pipelines.
Furthermore, actuated valves are also known as automatic valves. These are valves that are often connected to electric motors, air or pneumatic systems, hydraulic systems, or solenoids, these kinds of valves make use of an actuator mechanism or machine to remotely control and automate their functions. Unlike the ordinary and conventional valves that require manual operation, that is, valves that require someone’s physical attendance to operate, an actuated valve, on the other hand, does not require such physical attendance to be operated.
Blending all the above together, an electric actuated butterfly valve also known as an electric automatic butterfly valve is a butterfly valve with an electrical mechanical powered valve that starts, regulates, and stops the fluid flow without anyone in physical attendance to operate or control when the valve starts or when the valve stops. In fact, the electric actuated butterfly valve is a type of butterfly valve that operates itself through an electric valve actuator for controlling its opening and closing. The electrical and mechanical actuator connected to the butterfly valve converts electricity supplied to it in either linear or rotary motion to open and close the lid (disk) of the butterfly valve. The electric actuated butterfly valve has several and numerous advantages over the traditional or conventional manual butterfly valves. For instance, the electric actuated butterfly valves aid the synchronization of multiple line valves, it also helps in remote isolation of fluid or liquid control, and the electric actuated butterfly valve is also desirable due to the safety it provides to prevent any possible misuse. The electric actuated butterfly valve is technologically advanced and easier to use. They can make fluid systems safer and easier to control.
Conclusively, the question now is, where can you get a quality of the above description of valves (electric actuated butterfly valve) in the USA? Adamant Valves manufacture and supply sanitary electric actuated butterfly valves of good quality and standards in different sizes and at competitive prices. Kindly visit our website at https://www.adamantvalves.com/electric-actuated-sanitary-butterfly-valves.html to view our various quality collections and make a purchase. You can also reach out to us via telephone at +1 (949) 407 8897 or send us an email at [email protected]
The post WHERE CAN I FIND THE BEST ELECTRIC ACTUATED BUTTERFLY VALVE MANUFACTURER IN THE USA appeared first on Adamant Valves.
]]>The post WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN SANITARY FITTINGS AND FIXTURES? appeared first on Adamant Valves.
]]>The general idea on fixtures and fittings is that fixtures include those objects or appliances that are attached to the building, that is, the object that is permanently fixed on the building and cannot be removed without causing damage to the building. They are static, immovable, and motionless. On the other hand, the knowledge is that fittings are those objects or appliances that are not fixed to the building other than using a screw or nail; they can be easily moved and detached. However, the differences between sanitary fixtures and sanitary fittings go beyond this elementary knowledge of fixtures and fittings although it could further help in explaining one from the other, the differentiation on this knowledge is not totally sound.
By way of definition, sanitary fitting or sanitary fixtures are those objects or things mostly used in applications and processes requiring a clean, healthy, or sterile process such as dairy products, food processes, pharmaceuticals, medical and chemical productions as well as personal hygiene etcetera. These objects and appliances are made to be easily maintained, cleaned; crack free and they are also made with polished contact surfaces. They are also made with materials to preserve their sterility and cleanliness in the course of usage. They are also easily sanitized and disinfected.

Distinctively, a major difference between the two is that, in the first part, sanitary fixtures are those sanitary objects or appliances that are fixed or attached. They are commonly referred to as sanitary furniture. They are static, immovable, and motionless. Sanitary fixtures are sanitary wares or furniture attached and installed in different parts of a building and they are permanently connected to a plumbing system to be used for the reception and discharge of water or waste. Examples of sanitary fixtures include water closet, lavatory or washbasin, urinal, floor drain, flushing cisterns, showers, faucets, hose bibs, bathtubs, dishwashers, sinks, laundry sink, drinking fountain, bidet to mention a few. These fixtures are made from dense, durable, and non-absorbent materials that do not harbor bacteria or allow germs to multiply such as cast iron, ceramics, sheet steel, non-ferrous metals, and alloys.
On the other hand, c also known as hygienic fittings or sanitary clamps are those objects or appliances used to seal, clamp and fasten two or more separate ends of sanitary fixtures from any crevices or gaps to maintain a high hygienic standard. In other words, sanitary fittings are used to create closures, linkages, and a secure connection between sanitary fixtures so as not to create any leaking site or gap that can harbor or lead to exposure of bacteria and germs. Examples of sanitary fittings are determined by the connection types such as ball and sleeve fittings, barbed fittings, cam-lock fittings, compression fittings, crimp fittings, end fittings, flanges, threaded fittings etcetera; It is also determined by the function of such fitting such as fittings which extends or terminate (for example, adapter, coupling, sleeve, union, cap, plug etc.), fittings which add or change directions (for example, elbow, tee, wye, cross), fittings which changes vessel size (for example, reducer and olet), and fittings which provide special connections (for example, nipple) it could also include Valves for regulating and controlling of flows (for example, gate valves, globe valves, angle valves, check valves – spring check valve and swing check valve – ball valves, metered valves, flow control valve, thermostatic valves, temperature relief valve, pressure reducing valve, flushometer, sensor operated valves), traps for preventing foul gas from sewers to back flow (for example, floor traps, gully traps, intercepting traps) etcetera.
In summary, sanitary fixtures are those wares, equipment, and furniture in place for clean and hygienic purposes while sanitary fittings are those objects and appliances used to connect these fixtures together to achieve a high standard of cleanliness free from germs and bacteria. Notwithstanding the above distinction between sanitary fixtures and sanitary fittings, based on the uses of each, it is noted that although sanitary fixtures and sanitary fittings are distinctively different, both work hand in hand and are essential in achieving a sterile and germ-free environment. Sanitary fixtures and sanitary fittings are both essential for unparalleled efficiency in achieving a high level of joint cleanliness which is critical to delicate productions as mentioned earlier.
The post WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN SANITARY FITTINGS AND FIXTURES? appeared first on Adamant Valves.
]]>The post How To Select Valves In Different Temperatures appeared first on Adamant Valves.
]]>They are designed to allow adequate control of fluid by allowing easy on and off and throttle the fluid flow to ensure that the operation and process are smooth and efficient. The importance of valves has increased over the years and they are used in different process industries.
Every valve has a different specification and is used for different purposes. Several factors must be considered before purchasing or using a valve. Users may be confused about what kind of valve to choose from a large selection of different valves.
Factors To Consider When Selecting A Valve For A Process
The following will help when selecting a control valve and will ease the selection process for your next project:
- Flow control characteristics: know the maximum and minimum pressure and the acceptable temperature that the fluid will be transferred. Knowing the maximum and minimum inlet and outlet pressure that the valve will handle will help you select a valve with the right specification that meets all of these requirements.
- Fluid to be transferred: the kind of fluid that is to be transferred in the process determines the specification of the valve to use. Control valves control the flow of fluids like natural gas, compressed air, steam, liquefied petroleum, hydraulic fluid, slurry, and water. The valve needs to be suitable for any of this kind of fluid.
- Compatibility with remote systems: the environment for certain processes may be hazardous, and as such, there will be a need for the process control to be done remotely. The kind of valve you select must be suitable for the remote process management systems. This will ensure easy remote control and monitoring.
How Temperature Affects Valve Selection
The temperature of the system media running through a valve and the ambient operating temperature of the process environment are significant factors that determine the kind of valve to use. The process may involve changing temperatures, or the temperature may be kept constant.
The valve selected must account for this temperature fluctuation to avoid expansion and contraction that may affect the flow of the process fluids and materials.
Metallic components can quickly lose strength at a very high temperature. This may affect their pressure ratings and reduce it as time goes on, so it is essential to select the right valve made from the right materials and meet the temperature specification and application needs.
How To Select Valves in Different Temperature?
While selecting a valve for different temperatures, it is vital to consider the material it is made of, the operating temperature of the flowing media, and the process temperature.
When choosing a valve in a high-temperature process, materials with low-temperature resistance should not be considered. The kind of valves to consider are ceramic-lined special valves with a cooling jacket structure. Water circulates in the cooling jacket and ensures that the internal metal of the valve remains in place and within the allowable stress range.
When choosing a valve for a process with a low temperature below -29℃, you should select a valve made of low-temperature resistant materials. These kinds of materials have very high toughness and a good heat capacity such that the cooling load from the action would not crack the valve.
Using Tri-Clamp Ball Valves in High-Temperature Applications
Tri-clamp valves have significant application in the brewery, winery, dairy, and food processing industries. These valves have significant uses in this industry because their specification matches the temperature changes that usually accompany these processes.
They are made from high-grade stainless steel to ensure adequate hygiene needed for the food manufacturing process. The tri-clamp ball valve is a kind of sanitary ball Valve. The tri-clamp ball valve is a popular piece of Brewers Hardware. The brewery’s valves are manufactured from high-grade 304 stainless steel and a polished finish. You can get quality tri-clamp ball valves from adamant valves.
Final thoughts
The selection of a valve based on temperature depends on the temperature of the fluid media and the ambient temperature of the processing equipment. Different valves are suitable for different temperatures.
Are you looking for high-quality stainless steel tri-clamp ball valves? Look no further. You can visit Adamant valves to get the best sanitary valves, including stainless steel ball valves, butterfly valves, shut off and invert, check and diaphragm valves for different applications in different temperatures. You can quickly contact any of our experts to help you with a valve option best suited for your system by calling us at (949) 407 8897.
The post How To Select Valves In Different Temperatures appeared first on Adamant Valves.
]]>The post Materials Used in Inlet and Exhaust Hygienic Valve appeared first on Adamant Valves.
]]>Hygienic valves are special valves made from materials with very high purity. They are common in food, beverage, and dairy manufacturing as these are processes that do not need any form of contamination. Medical, chemical, pharmaceutical processes also require hygienic valves.
Hygienic valves are generally crucial in processes that require a high level of cleanability. Standard features of hygienic valves include easy cleaning, crevice-free, and a well-polished contact surface.
Hygienic valves are different from aseptic valves. We use aseptic valves mostly in industries that require very high purity levels. They are used in injection drugs, cosmetics, microelectronics, and others.
Aseptic valves are mainly used to control processes and minimize contamination from different environmental sources.
The valves used and the design is fundamental in sanitary applications.
Types of Hygienic Valves
The different valves used in manufacturing processes require very high purity and easy cleanability. They are the globe, pinch, knife or gate, needle, butterfly, ball diaphragm, and plug valves.
- Diaphragm valves: this kind of valve is related to pinch valves, but the valve body has a diaphragm made from an elastomer rather than an elastomeric liner. With this kind of diaphragm, flow is easily separated from the closure element.
- Pinch Valves: this kind of valve makes use of a flexible elastomer in its lining that can easily be pinched to close and cut off the flow and reduce the fluid pressure. Pinch valves are used to control linear flow and as a throttling device using their on and off mechanism.
- Gate or Knife valves: these are Linear motion kinds of valves. The valve uses a mechanism that involves a flat closure element that slides into the flow stream and shuts off flow. There are two types of gate valves: parallel and wedge-shaped.
- Needle valves: These have a small, slender, and pointed end at the end of the valve stem. Lowering this tapered end restricts fluid flow through the valve.
- Globe valves: the globe valves are generally linear motion valves with rounded bodies. These valves are used in the industry and other manufacturing processes to regulate fluid flow both on/off and throttling services.
- Butterfly sanitary valves: These valves control fluid flow where high sensitivity is needed. They are quick opening valves and are used as throttling devices to manage fluid flow effectively.
- Ball valves: These valves have a large sphere with a central hole equal to the inside diameter of the pipe where there is flow. As the ball rotates inside the valve, it restricts or permits fluid flow through it.
Specifications of the Hygienic Valves
There are certain important specifications that hygienic valves should have. This includes the diameter, working pressure, and operating temperature. We can measure the valve diameter by measuring the distance across the Inlet or outlet port. The working pressure is the designated pressure at which the valve operates. The operating temperature is the stipulated temperature that the valve can work at. The media types that the sanitary valve can regulate include glasses, liquids, and suspended solids.
Materials Used in the Hygienic Valves
Hygienic valves are made with a specific material that ensures their cleanability. Metals and plastics are the two common materials used in Inlet and exhaust hygienic valves. Examples of metallic materials that give quality hygienic valves are brass, bronze, copper, cast iron, ductile iron, stainless steel, and steel. Examples of plastic choices include PVC and CPVC.
Typical end connections of the hygienic valves include threaded, socket-weld, or buttweld. The different actuation of hygienic valves includes electric, pneumatic, hydraulic, and manual.
The Inlet and exhaust of a valve need to be resistant to high temperature, corrosion, and fatigue. The valve seat can be hardened with molybdenum steel to meet this requirement. The valve spindle can be made from molybdenum chrome alloy with a layer of stellite welded onto the seating face — a heat-resistant nimonic alloy valve head.
Stainless steel valves are usually chrome-plated to improve their lubricity and reduce the wearing of the stem.
Final Thoughts
The kind of material used in the Inlet or outlet of a hygienic valve ensures a high level of cleanability and purity not to contaminate the flowing fluid. Suitable materials include stainless steel, brass, copper, and plastics.
Are you looking for high-quality hygienic and sanitary valves? Look no further. You can visit Adamant Valves to get the best hygienic valves made from stainless steel, brass, bronze, and quality plastic materials. You can contact us to get yours or speak to any of our experts to get a suitable material for your hygienic valve by calling (949) 407 889.
The post Materials Used in Inlet and Exhaust Hygienic Valve appeared first on Adamant Valves.
]]>